1 | import os |
cif格式转换vasp格式python脚本(cif_to_vasp)
依赖
python 3
脚本内容
1 | from ase import io |
基于ase的三行脚本即可将.cif文件转换为vasp格式文件,然而由于ase包的问题,转换后的POSCAR文件第六行缺少对应的元素符号,需额外通过python脚本处理生成好的POSCAR文件来达到最终目的。
完整代码如下:
1 | from ase import io |
可能存在的问题
- windows平台,MS建好模型后通过坚果云共享到MAC系统中,cif一定几率变成二进制文件报错
材料光学性质(一)
光学性质基础
wave particle duality(by Einstein)
photoelectric effect:the emission of electrons or other free carriers when electromagnetic radiation, like light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner can be called photoelectrons.
Plank equation
E=hv, h=6.626× 10-34 m2 kg / s
The de Broglie Relations
p=hv=hc/λ
Standing and Traveling waves
驻波(standing wave或stationary wave)为两个波长、周期、频率和波速皆相同的正弦波相向行进干涉而成的合成波。与行波不同,驻波的波形无法前进,因此无法传播能量,故名之。驻波最大值和最小值在某一固定点不动
行波(travelling wave)是指平面波在传输线上的一种传输状态,其幅度沿传播方向按指数规律变化,相位沿传输线按线性规律变化。
波是y=sinx,行波就是波要在走,y=sin(x-t)就可表示行波, 可以看到t=0时波是y=sinx, t=1时y=sin(x-1). 每一刻波都在往右走,这就是行波。y=sin(x+t),也是行波,但是在往左走。
如果俩个完全一样,仅方向不一样的行波y=sin(x-t)和y=sin(x+t)相遇,公式变成y=2sinxcost,可以看到只要x=0,或者半波长整数倍的时候,y=0,代表这时不管t怎么变,这些点永远不动,这些点就是驻波的波节,在看除波节外的任一点,t=0时,y达到正幅值,t=1/4周期时,y=0,这时波是一条直线,所有值都是零,t=1/2周期时,y达到负幅值,所以y=2sinxcost就是驻波,波节不动,其余地方一直在震动。
???相速度和群速度???
some quiz
- Can gravity bend the light?(Yes, the star is not at the position we observe because of the sun)
- What is the princeple of fiber?(Total reflection)
- Are there any loss during the transpotation of fiber? If yes, where is the loss from?(yes, they from:a.any materials can absorb some light. b.the fiber is not all straight along the whole road. if there is a corner, 90 degree, which do not satisfy the prerequest of the total reflection. Herein, there will be some loss.)
- What are the conditions for total reflection to occur?(a.from n larger medium to n small medium, n is refraction index b. staify critical angle)
- What’s the difference between mechanical wave and electromagnetic wave?(transportation medium)
- Waht is the wave number?(k=2π/λ)
words
Isotropic:各向同性
Sodium:钠
copper:铜
Zinc:锌
Prism:棱镜
reflection:反射
refraction:折射
Python常用技巧总结
enumerate
enumerate() 函数用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在 for 循环当中,可减少命名额外的变量。索引默认从0开始。
1 | # 普通的for循环 |
Numpy
1 | data.shape #数组形状 |
Pandas
1 | data.iat[0,0] #特定位置元素 |
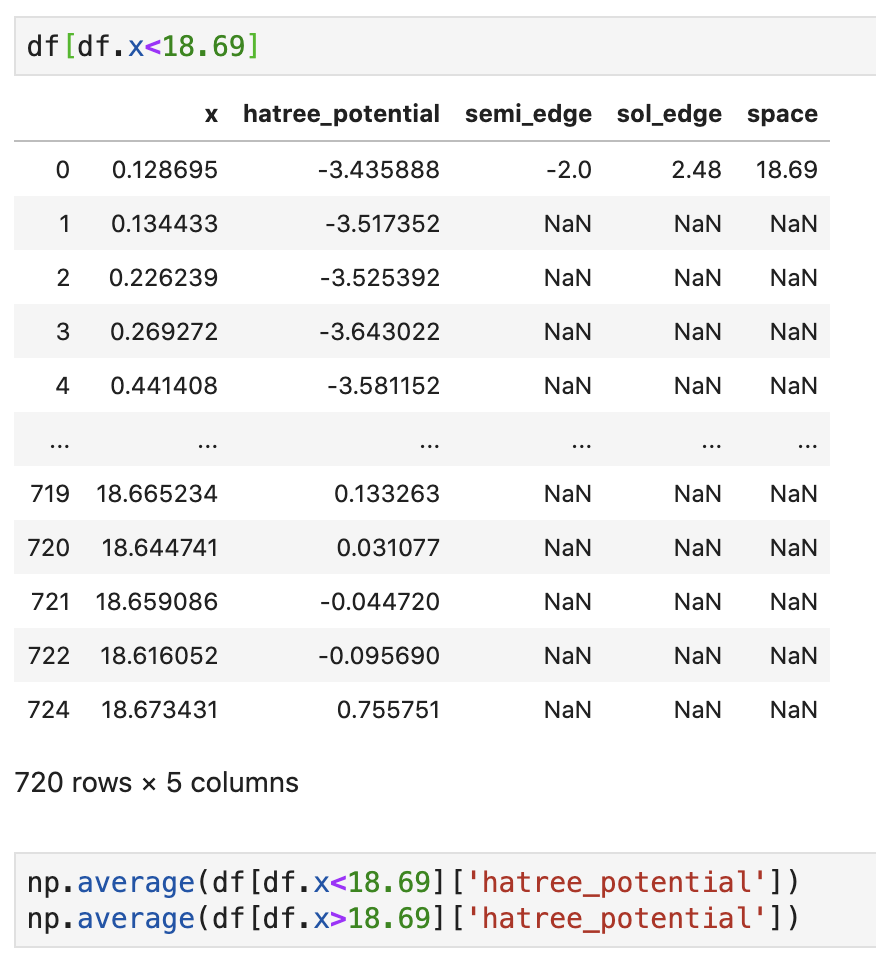
筛选x列小于18.69的数据并且对第二列求平均
绘图
1 | # 散点图,alpha透明度,color为内部颜色,color=' '无内部颜色,s标记大小 |
对不收敛vasp结果将CONTCAR改为POSCAR继续计算bash脚本
bash基础语法
Kmeans聚类算法实例-31省城市消费水平
本文字数: 0 阅读时长 ≈ 1 分钟
无监督学习简介-聚类和降维
本文字数: 606 阅读时长 ≈ 1 分钟
无监督学习的目标
利用无标签的数据学习数据的分布或数据与数据之间的关系被称作无监督学习。
有监督学习和无监督学习的最大区别在于数据是否有标签
无监督学习最常应用的场景是聚类(clustering)和降维(Dimension Reduction)
聚类(clustering),就是根据数据的“相似性”将数据分为多类的过程。评估两个不同样本之间的“相似性”,通常使用的方法就是计算两个样本之间的“距离”。使用不同的方法计算样本间的距离会关系到聚类结果的好坏。距离的常见算法有欧氏距离,曼哈顿距离,马氏距离,夹角余弦。
降维,就是在保证数据所具有的代表性特性或者分布的情况下,将高维数据转化为低维数据的过程。降维可以精简数据和数据可视化。
聚类常见算法(sklearn.cluster)
| 算法名称 | 参数 | 可拓展性 | 相似性度量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-means | 聚类个数 | 大规模数据 | 点间距离 |
| DBSCAN | 邻域大小 | 大规模数据 | 点间距离 |
| Gaussian Mixtures | 聚类个数及其他超参 | 复杂度高,不适合处理大规模数据 | 马氏距离 |
| Birch | 分支因子,阈值等其他超参 | 大规模数据 | 两点间的欧式距离 |
常见降维算法(sklearn.decomposition)
| 算法 | 参数 | 可拓展性 | 适用任务 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 所降维度及其他超参 | 大规模数据 | 信号处理等 |
| FastICA | 所降维度及其他超参 | 超大规模数据 | 图形图像特征提取 |
| NMF | 所降维度及其他超参 | 大规模数据 | 图形图像特征提取 |
| LDA | 所降维度及其他超参 | 大规模数据 | 文本数据,主题挖掘 |
sklearn库中常用数据集及调用方法
常用数据集
| 数据集名称 | 调用方式 | 适用算法 | 数据规模 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 波士顿房价数据集 | load_boston() | 回归 | 506*13 |
| 鸢尾花数据集 | load_iris() | 分类 | 150*4 |
| 糖尿病数据集 | load_diabetes() | 回归 | 442*10 |
| 手写数字数据集 | load_digits() | 分类 | 5620*64 |
| Olivetti 脸部图像数据集 | fetch_olivetti_faces() | 降维 | 4006464 |
| 新闻分类数据集 | fetch_20newsgroups() | 分类 | - |
| 带标签的人脸数据集 | fetch_lfw_people() | 分类;降维 | - |
| 路透社新闻语料数据集 | fetch_rcv1() | 分类 | 804414*47236 |
sklearn.datasets.load_boston
其重要参数为:
•return_X_y:表示是否返回target(即价格),默认为False,只返回data(即属性)。
1 | >>> from sklearn.datasets import load_boston |
sklearn库的基本功能
分类任务
| 分类模型 | 加载模块 |
|---|---|
| 最近邻算法 | neighbors.NearestNeighbors |
| 支持向量机 | svm.SVC |
| 朴素贝叶斯 | naive_bayes.GaussianNB |
| 决策树 | tree.DecisionTreeClassifier |
| 集成方法 | ensemble.BaggingClassifier |
| 神经网络 | neural_network.MLPClassifier |
回归任务
| 回归模型 | 加载模块 |
|---|---|
| 岭回归 | linear_model.Ridge |
| Lasso回归 | linear_model.Lasso |
| 弹性网络 | linear_model.ElasticNet |
| 最小角回归 | linear_model.Lars |
| 贝叶斯回归 | linear_model.BayesianRidge |
| 逻辑回归 | linear_model.LogisticRegression |
| 多项式回归 | preprocessing. PolynomialFeatures |
聚类任务
| 聚类方法 | 加载模块 |
|---|---|
| K-means | cluster.KMeans |
| AP聚类 | cluster.AffinityPropagation |
| 均值漂移 | cluster.MeanShift |
| 层次聚类 | cluster.AgglomerativeClustering |
| DBSCAN | cluster.DBSCAN |
| BIRCH | cluster.Birch |
| 谱聚类 | cluster.SpectralClustering |
降维人物
| 降维方法 | 加载模块 |
|---|---|
| 主成分分析 | decomposition.PCA |
| 截断SVD和LSA | decomposition.TruncatedSVD |
| 字典学习 | decomposition.SparseCoder |
| 因子分析 | decomposition.FactorAnalysis |
| 独立成分分析 | decomposition.FastICA |
| 非负矩阵分解 | decomposition.NMF |
| LDA | decomposition.LatentDirichletAllocation |
能斯特方程
基本概念梳理
- $E_o$, the standard equilibrium potential (or standard electrode potential), is defined as the equilibrium potential of an electrode reaction when all components are in their standard states, measured against the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE).
标准电极电位是反应处在标准状态下(298K,所有离子的浓度都是1mol/L),的平衡电位,其数值可在标准电位表中查出,也可以根据热力学上的数据自行运算。
eg:在腐蚀电化学原理(曹楚南)一书中,常见金属相对于H电极的标准平衡电位是:
| 反应 | SHE(V) |
|---|---|
| $Li$=$Li^+$+$e^-$ | -3.024 |
| Ca=Ca^2+^+2e^-^ | -2.87 |
| Mg=Mg^2+^+2e^-^ | -2.34 |
| Al=Al^3+^+3e^-^ | -1.67 |
| Zn=Zn^2+^+2e^-^ | -0.762 |
自己计算的方法如下,首先在德国爱德华久保热力学和物质动力学基金会找到对应离子的化学势;
网站的数据遵循标准:(1)在标准状态下 (T = 298 K, p = 101,3 kPa),(2)在溶液标准浓度下 (1000 mol/m3),(3)处于理想状态下,没有分子间相互作用的气体或溶解物质,(4)由元素的天然同位素组成的所有物质。
单位μ代表kJ/mol,1 eV/atom = 96.49 kJ/mol,网站中“,”代表小数点
| 元素 | 网站数据(μ) | ev/atom | 计算平衡电位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li^+^ | -293.80 | -3.0449 | -3.0449 |
| Ca^2+^ | -553.04 | -5.7316 | -2.8658 |
| Mg^2+^ | -456.01 | 4.726 | -2.363 |
| Al^3+^ | -485.34 | -5.03 | -1.6767 |
| Zn^2+^ | -147.03 | -1.5238 | -0.7619 |
- $E_e$,equilibrium potential of an electrode, 平衡电极电位。大多数时候,反应都无法在标准状态下进行。由于此时离子浓度较标准状态下发生变化,平衡随之移动,平衡电位也会相继发生改变。
- 反应的氧化态和还原态,注意能斯特方程的浓度方法,+氧化态在上面的浓度
Oxidised State + ne- ⇌ Reduced State
能斯特方程
The Nernst equation links the equilibrium potential of an electrode, Ee, to its standard potential(standard equilibium potential), E0, and the concentrations or pressures of the reacting components at a given temperature. It describes the value of Ee for a given reaction as a function of the concentrations (or pressures) of all participating chemical species.
In its most fundamental forms, the Nernst equation for an electrode is written as:
$E_e$=$E_0$+$\frac{RT}{zF}ln\frac{[Oxidised]}{[Reduced]}$
or
$E_e$=$E_0$+$\frac{2.303RT}{zF}log\frac{[Oxidised]}{[Reduced]}$
or
$E_e$=$E_0$+$\frac{2.303$k_b$T}{ze}log\frac{[Oxidised]}{[Reduced]}$
[Click here for a full derivation of Nernst equation – popup]
R is the universal gas constant (8.3145 J K-1 mol-1)
T is the absolute temperature
z is the number of moles of electrons involved in the reaction as written
F is the Faraday constant (96 485 C per mole of electrons)
The notation [reduced] represents the product of the concentrations (or pressures where gases are involved) of all the species that appear on the reduced side of the electrode reaction, raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients. The notation [oxidised] represents the same for the oxidised side of the electrode reaction.
Explanation of Activity